Abstract
While commendable progress has been made in user-centric research on mobile assistive systems for blind and low-vision (BLV) individuals, references that directly inform robot navigation design remain rare.
To bridge this gap, we conducted a comprehensive human study involving interviews with 26 guide dog handlers, 4 white cane users, 9 guide dog trainers, and 1 O&M trainer, along with 15+ hours of observing guide dog-assisted walking. After de-identification, we open-sourced the GuideData dataset to promote human-centered development.
Building on insights from this formative study, we developed GuideNav, a vision-only, teach-and-repeat navigation system. Inspired by how guide dogs are trained and assist their handlers, GuideNav autonomously repeats a path demonstrated by a sighted person using a robot.
The system constructs a topological representation of the taught route, integrates visual place recognition with temporal filtering, and employs a relative pose estimator to compute navigation actions — all without relying on costly, heavy, power-hungry sensors such as LiDAR.
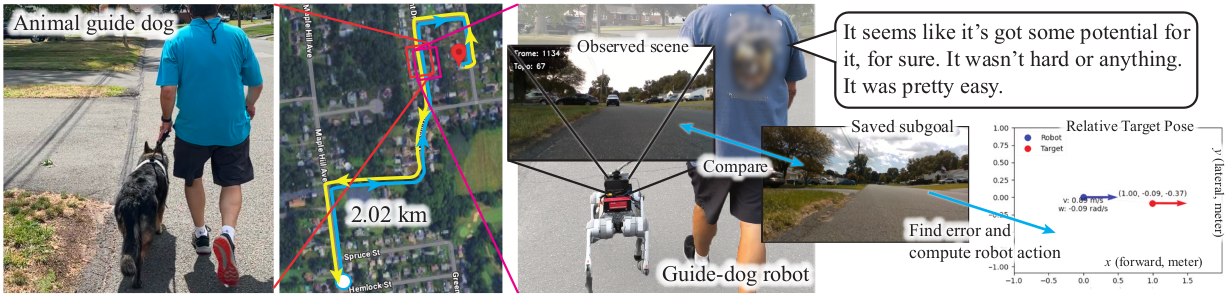
In field tests, GuideNav consistently achieved kilometer-scale route following across five outdoor environments, maintaining reliability despite noticeable scene variations between teach and repeat runs.
A user study with 3 guide dog handlers and 1 guide dog trainer further confirmed the system's feasibility, marking (to our knowledge) the first demonstration of a quadruped mobile system retrieving a path in a manner comparable to guide dogs.
Key Contributions
- Comprehensive Formative Study: Interviews with 40 participants (26 guide dog handlers, 4 white cane users, 9 guide dog trainers, 1 O&M trainer) and 15+ hours of observation to inform guide robot design.
- Open-Source Dataset: De-identified interview and observation data (GuideData) released to promote human-centered assistive technology development.
- Vision-Only Navigation: Teach-and-repeat system using only cameras — no LiDAR or depth sensors required.
- Robust Field Performance: Kilometer-scale route following across 5 diverse outdoor environments with scene variations.
- First Quadruped Guide Robot Demo: To our knowledge, the first demonstration of a quadruped robot retrieving paths comparable to guide dogs.
GuideNav Pipeline
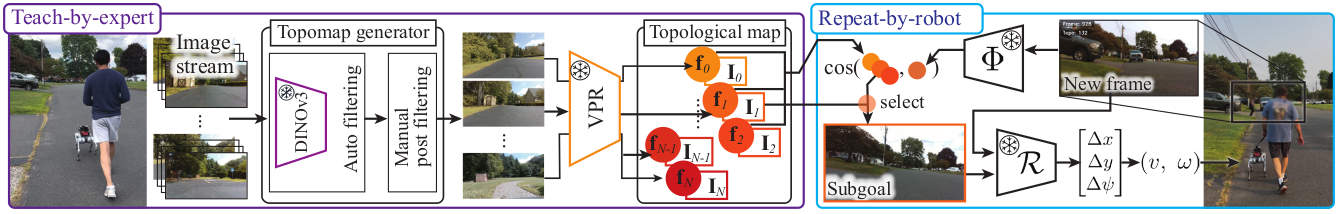
Teach Phase: A sighted person walks the desired route while the robot captures images and builds a topological map representation of the environment.
Repeat Phase: The robot uses visual place recognition (VPR) with temporal filtering to localize itself within the taught map, then employs a relative pose estimator to compute navigation actions and autonomously follow the demonstrated path.
Our vision-only approach eliminates the need for expensive sensors like LiDAR, making the system more practical and accessible for real-world deployment.